DataScience_Examples
All about DataSince, DataEngineering and ComputerScience
View the Project on GitHub datainsightat/DataScience_Examples
What is good code?
Three Pillars of Code
- Readable
- Scalable
- Time Complexity
- Space Complexity
Data Structures + Algorithms = Programs
Big O
Characterise code in terms of runtime and memory requirements.
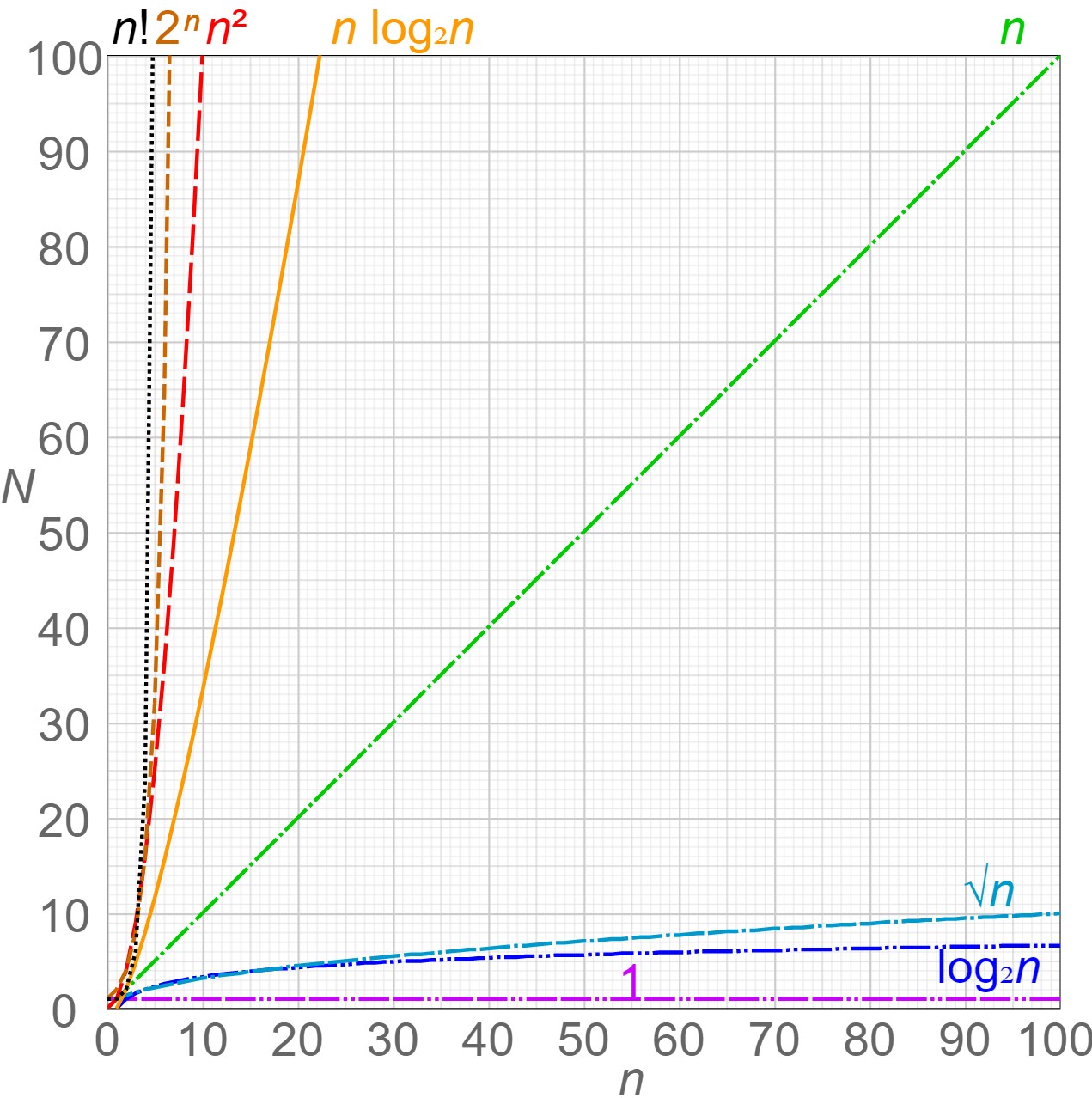
- O(1) Constant - no loops
- O(log N) Logartihmic - search algorithms
- O(n) Linear time - for loops
- O(n * log(n)) log linear - sorting operations
- O(n ^ 2) Quadratic - nested loops
- O(2 ^ n) Exponential - recursive
- O(n!) Factorial time - add loop for every element
Rules
- Worst case
- Remove constants
- Different terms for inputs O(a + b), Nested arrays O(a * b)
- Drop non dominants
Iterating through half the operations is still O(n)
Two separate collections: O(a * b)
Time Complexity
What takes time?
- Operations (+, -, *, /)
- Comparisons (<, >, ==)
- Looping
- Function calls
Examples
function funChallenge(input) {
let a = 10; //O(1)
a = 50 + 3; //O(1)
for (le ti = 0; i < input.length; i++) { //O(n)
anotherFunction(); //O(n)
let stranger = true; //O(n)
a++; //O(n)
}
return a; //O(1)
}
funCallenge(); //O(3*1 + 4*n) = O(n)
function anotherFunChallenge(input) {
let a = 5; //O(1)
let b = 10; //O(1)
let c = 50; //O(1)
for (let i = 0; i < input; i++) {
let x = i + 1; //O(n)
let y = i + 2; //O(n)
let z = i + 3; //O(n)
}
for (let j = 0; j < input; j++) {
let p = j * 2; //O(n)
let q = j * 2; //O(n)
}
let WhoAmI = 'I don't know"; //O(1)
}
anotherFunChallenge(); //O(4*1 + 3*n + 2*n) = O(n)
function compressBoxesTwice(boxes1, boxes2) {
boxes.forEach(function(boxes)) {
console.log(boxes);
}
boxes.forEach(function(boxes)) {
console.log(boxes);
}
}
compressBoxesTwice() //O(a + b)
function compressBoxesTwice(boxes1, boxes2) {
boxes.forEach(function(boxes)) {
console.log(boxes);
boxes.forEach(function(boxes)) {
console.log(boxes);
}
}
}
compressBoxesTwice() //O(a * b)
Space Complexity
Memory
- Heap (Variables)
- Stack (Function calls)
What causes space complexity?
- Variables
- Data Structures
- Function Calls
- Allocations
Example
function booo(n) {
for (let i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
console.log('booo');
}
}
booo([1,2,3,4]) // O(1)
function arrayOfHinNTimes(n) {
let hiArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
hiArray[i] = 'hi';
}
return hiArray;
}
arrayOfHinNTimes(6); // O(n)
//Find 1st, Find Nth...
const array = ['hi','my','teddy'];
array[0]; //O(1)
array[array.length - 1]; //O(1)
//Find 1st, Find Nth...
const array = [{
tweet: 'hi',
date: 2012
}, {
tweet: 'my',
date: 2014
}, {
tweet: 'teddy',
date: 2018
}]; //O(n^2) ... Nested Loop